Harnessing Artificial Intelligence to accelerate sustainable development

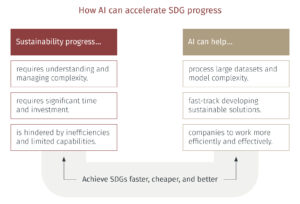
Despite global efforts to combat climate change, the world is not on track to meet the Paris Agreement’s crucial goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C. Progress has also been slow against the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) the UN introduced in 2015 with the aim of ending poverty, protecting the planet and ensuring peace and prosperity for all by 2030. With six years left, only around 17% of these goals are on track.2 New tools and innovative solutions are urgently needed to tackle multifaceted challenges. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) comes in: It excels at processing vast amounts of diverse data, allowing it to facilitate scenario development, accelerate strategy evaluation, optimise operations and monitor progress, allowing for deeper insights into complex systems.
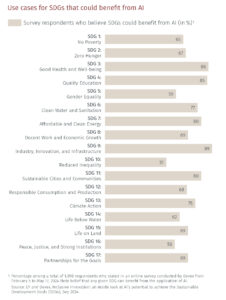
AI is already making significant contributions to all the SDGs in areas such as healthcare, food aid and solving supply chain issues. One of its most essential roles lies in tackling climate change, in alignment with SDG 13 (Climate Action). AI has the potential to drive climate progress across key areas including:3
- Mitigation: AI can help to reduce and remove greenhouse gas emissions by optimising energy consumption, enhancing efficiency and facilitating renewable energy development.
- Adaptation and resilience: AI can help prepare for and respond to the impacts of climate change through early-warning systems, optimised resource allocation and scenario modelling.
- Foundational capabilities: AI can advance climate economics, enhances education and fosters innovation, enabling more accurate predictions and supporting new technologies.
In many areas, there already is a measurable real-world impact. For example, AI-powered tools now provide actionable flood forecasts through accurate projections well in advance of extreme weather events.4 In agriculture, AI helps forecast weather and crop yields, develop sustainable pest control and predict soil erosion. Additionally, it can identify low-carbon compounds to replace high-emission materials in engineering.
AI also has transformative potential at the company level, and nearly 75% of large businesses have already integrated it into their strategies.2 It can conduct advanced data analysis, provide intelligent decision support and increase efficiency. By applying AI capabilities, companies can accelerate sustainable development across areas including operational efficiency and reduced environmental impacts, sustainable value chains, and risk management and resilience.2
While AI holds great promise, it also entails certain risks. Without responsible oversight, AI could cause environmental and social harm. It can generate biased outputs – including through the underrepresentation of marginalised groups in training data –, produce factual errors, increase resource consumption and potentially accelerate job displacement and the spread of misinformation.
Nevertheless, AI has significant potential to boost progress towards the SDGs. By effectively integrating it into our global strategies and fostering collaboration among governments, businesses and communities, we can address challenges more efficiently. Harnessing AI’s capabilities can help us to bridge the gap between our current efforts and the ambitious targets we have set.
1 Sustainable Development Solutions Network, Sustainable Development Report 2024
2 United Nations Global Compact and Accenture, Gen AI for the Global Goals, 2024
3 BCG and Google, Accelerating Climate Action with AI, Nov 2023
4 McKinsey, AI for social good: Improving lives and protecting the planet, May 2024
Read the full article here.
– Author: Melanie Beyeler, Senior Portfolio Manager, EFG International
– This contribution is brought to you by EFG, a valued silver event partner of Building Bridges 2024.